Web security tips: How PAN-DB works
PAN-DB is our URL and IP database, designed to fulfill an enterprise’s web security needs. PAN-DB is tightly integrated into PAN-OS, providing you Advanced Persistent Threat (APT) protection with high-performance beyond traditional URL filtering.
Traditional URL filtering is intended to control unwanted web surfing such as non-business or illegal sites, but it usually doesn’t cover up to the minute malicious web sites such as newly discovered malware site, exploit site or command and control sites. Let me explain how PAN-DB works for you.
How PAN-DB maximizes your URL lookup performance
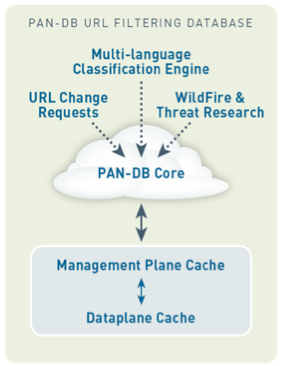
Figure1. PAN-DB classification and cache system
PAN-DB Core: The PAN-DB Core, located in the Palo Alto Networks threat intelligence cloud, has a full URL and IP database to cover web security needs.
Seed database: When the PAN-DB is enabled on your firewalls, a subset of the full URL database is downloaded from the Palo Alto Networks threat intelligence cloud to firewalls based on the selected geographic region. Each region contains a subset of the URL database that includes URLs most accessed for the given region. This regional subset of the URL database allows the firewalls to store a much smaller URL database, in order to greatly improve URL lookup performance. You can download a seed database by region to the each firewall from our Panorama centralized management system as well.
Management plane cache: The seed database is placed into the management plane (MP) cache to provide quick URL lookups. The MP cache will pull more URLs and categories from the PAN-DB core as users access sites that are not currently in the MP cache. If the URL requested by a user is “unknown” to Palo Alto Networks, the URL will be examined, categorized, and implemented as appropriate.
Dataplane cache: A dataplane cache (DP) contains the most frequently accessed sites for quicker URL lookups.
Malicious URL database delivered from WildFire
Millions of URLs and IPs are classified in a variety of ways. In addition to the “Multi-language classification engine” and the “URL change request from users,” PAN-DB receives malicious URL and IP information from WildFire. Examples of malicious URL and IP database are shown below.
- Malware Download URL and IP address: Prevent from downloading malware.
- C&C URL and IP address: Disable malware communications.
The malicious URLs are generated as WildFire identifies unknown malware, zero-day exploits and APTs by executing them in a virtual sandbox environment.
PAN-DB will block malicious URL with low latency
PAN-DB has a superior mechanism to lookup URL faster, and then you will get URL category information without sacrificing the throughput.
The malicious URLs are generated as WildFire identifies unknown malware, zero-day exploits, and Advanced Persistent Threats (APTs) and executes them in a virtual sandbox environment. The ongoing malicious URL updates to PAN-DB allows you to block malware downloads and disable malware command and control communications.
By utilizing malicious URL database, you can block variety of malicious web access and communication without compromising web access performance.
To learn more about web security, please visit our resource page, Control Web Activity with URL Filtering.
Related Blogs
Subscribe to the Newsletter!
By submitting this form, you agree to our Terms of Use and acknowledge our Privacy Statement. Please look for a confirmation email from us. If you don't receive it in the next 10 minutes, please check your spam folder.